Differences and precautions in processing copper busbars vs. aluminum busbars
When punching, cutting, and bending copper and aluminum busbars, to avoid obvious bright bands/shear bands or even burrs on the processed cross-section, it is recommended to establish two independent parameter libraries (“Copper-Lib” and “Aluminum-Lib”) in the CNC system of the busbar machine, and to distinguish between copper busbar-specific molds and aluminum busbar-specific molds for the…
When high and low voltage switchgear manufacturers or electrical panel factories use busbar machine (related: 什麼是母線機?) to process copper and aluminum busbars, if the technical engineers do not understand the physical properties (hardness, ductility, resilience) of the two metal materials, the finished product will be uncontrollable when punching, cutting and bending copper and aluminum busbars. This will result in obvious bright zone/shear zone, or even burrs, which will affect the quality and service life of the switchgear or electrical panel.
Copper busbars and aluminum busbars have significantly different physical properties, resulting in drastically different processing parameters and precautions. The following is a detailed analysis of the differences and specific precautions for machining these two materials in busbar machine processing:
Physical properties of copper busbars and aluminum busbars
| 特徵 | Copper busbar | Aluminum busbar | Processing impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Higher | Lower (Softer) | Copper requires greater shearing and punching pressure; aluminum tends to stick to the tool. |
| Ductility | Excellent | Good, but Brittle and easily broken | Copper can be bent with a small radius angle; aluminum is prone to cracking under small radius angles. |
| Rebound Rate | Smaller, more stable | Large and unstable | The bending angle compensation for aluminum needs to be set to a larger value. |
| Surface | Average scratch resistance | Very easy to scratch | Aluminum busbars require extra care during feeding and processing. |
When punching copper busbars, the cut surface is usually clean with few burrs. However, due to the hardness of copper, the punching die head wears relatively quickly, requiring regular checks of the punch’s sharpness.
When punching aluminum busbars, the soft and sticky nature of aluminum makes it prone to **Galling**, where aluminum shavings adhere to the punch or die. Therefore, the die must be cleaned more frequently to prevent shavings buildup that could cause punching deformation or die jamming. For aluminum busbars, the die clearance can be appropriately reduced to ensure a smooth hole wall.
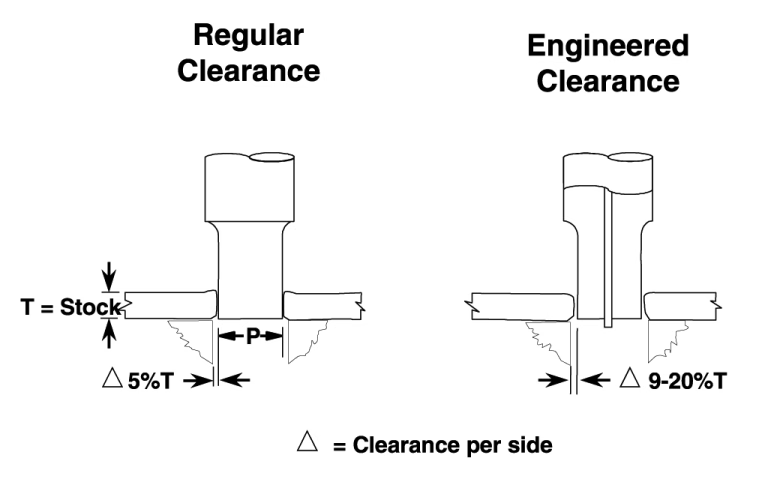
Differences and precautions in punching unit processing
When punching copper busbars, the cut surface is usually clean with few burrs. However, due to the hardness of copper, the punching die head wears relatively quickly, requiring regular checks of the punch’s sharpness.
When punching aluminum busbars, the soft and sticky nature of aluminum makes it prone to **Galling**, where aluminum shavings adhere to the punch or die. Therefore, the die must be cleaned more frequently to prevent shavings buildup that could cause punching deformation or die jamming. For aluminum busbars, the die clearance can be appropriately reduced to ensure a smooth hole wall.
尖端: Requirements for die clearance when punching copper and aluminum busbars.
Differences and precautions in cutting unit processing
Copper busbars have high shear resistance and typically have a bright cross-section. However, one crucial point must be noted: ensure the shear blade is sharp. If the blade is dull, the copper busbar cross-section is prone to chipped corners or severe burrs.
Aluminum busbars, on the other hand, have low shear resistance but are easily deformed (flattened). During shearing, the pressure of the clamping foot (pressing device) must be moderate. Excessive pressure may leave indentations on the aluminum busbar surface, while insufficient pressure will result in a non-perpendicular cross-section.
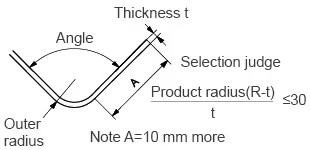
Differences and Precautions in Bending Unit Processing – The Most Critical Step
This is the process with the biggest difference between the two, mainly in the **bending radius (R angle) and springback compensation**.
Copper busbars have good ductility and can usually use smaller R angle dies (e.g., R = busbar thickness), making them less prone to cracking. Their springback angle is smaller (usually around 3°-5°), making CNC control easier.
Aluminum busbars (especially hard aluminum) are extremely prone to cracking when stretched on the outside. This requires that **larger bending R angle dies must be used when processing aluminum busbars**, and **it is generally recommended that the R angle be ≥ 1.5 to 2 times the aluminum busbar thickness**. The springback rate of aluminum is also usually greater than that of copper (depending on the aluminum grade), and there is significant batch-to-batch variation. If the target angle is 90°, copper may only need to be bent to 92°, while aluminum may need to be bent to 95° or even more to spring back to 90°. It is recommended to set up a separate material library parameter for aluminum busbars in the CNC system.
Operation and maintenance precautions
- **Mold Protection (Recommended)**
- Although copper and aluminum can use the same set of molds, to prevent **electrochemical corrosion** (copper-aluminum contact accelerates corrosion in humid environments), it is recommended to use separate molds for copper and aluminum whenever possible. If mixing is unavoidable, thoroughly clean any metal shavings from the molds before switching materials.
- **Surface Protection:**
- Aluminum busbars are very easily scratched. When dragging aluminum busbars for positioning, avoid dragging them hard on the worktable. It is recommended to apply anti-abrasion rubber pads to the worktable of the busbar machine or use an auxiliary bracket with rollers.
- **Lubrication:**
- When punching holes in aluminum busbars, apply a small amount of special lubricating oil or alcohol to the punch to reduce adhesion and improve demolding smoothness.
Summary and Recommendations
If you are conducting mass production, it is recommended to establish two independent parameter libraries (“Copper-Lib” and “Aluminum-Lib”) in the CNC system of the busbar machine, and to distinguish between copper busbar-specific dies and aluminum busbar-specific dies for the punching unit. It is crucial to record the different bending elastic coefficients and die radius selections for both. This way, when switching materials, you can simply call up the relevant parameters with one click, eliminating the need for repeated die trials.
推薦文章
中國進出口商品交易會推薦 SUNSHINE® 母線加工機
聯絡我們從中國 SunShine® 取得最佳母線機報價
快速審核您的需求並有效率地提供專業的技術解決方案! 我們傾聽並關心您的需求,我們的工作人員將在 24 小時內透過電子郵件和電話與您聯繫。
哪裡可以買到品質可靠的母線加工機?
我們是中國母線機械製造商和工廠。請聯絡我們的銷售經理 Lisa (信箱: lisa@busbarmachine.co)並提供母線圖紙或產品樣品。我們將評估並為您做出最佳推薦產品或產品。母線機客製化(功能或PLC),並提供完整的技術報價。
預算有限,購買什麼型號的母線加工機?
山鑫擁有經濟型母線加工設備及高效能全自動數控母線加工設備,並可依客戶的生產場地、母線加工需求及資金預算,客製化技術報價方案。請聯絡我們的專業銷售經理Lisa (信箱: lisa@busbarmachine.co)取得技術支援及報價服務。
除了母線機,你們還提供母線模具嗎?
我們通常會贈送一些母線模具,包括彎曲,切割,沖孔和壓花等。
機器的電壓是多少?
標準電壓為3相、220V、60Hz。電壓可以根據客戶要求定制。
交貨時間多長?
這取決於我們的庫存情況和母線機的複雜性。正常情況下,如果我們有合適的母線庫存,則最多需要 3 天的時間,而對於需要從頭到尾製造的母線機器,我們通常需要大約 7 到 15 天的時間。對於複雜的機器或母線生產線,我們需要大約20到30天。
你們的保固政策是什麼?
在正確使用的情況下,我們提供 12 個月的保固。將在保固期內提供遠端協助並免費發送替換零件。
你們的付款條件是什麼?
我們的付款條件是30%預付款和出貨前70%餘款。
您能派工程師到海外進行現場安裝、訓練或測試服務嗎?
所有機器在發貨前都會經過測試和調試。原則上我們只提供遠端調試服務和遠端技術援助。如果是母線生產線,我們會有技術人員在現場進行現場服務。
我們可以參觀你們的工廠或進行現場檢查嗎?
我們非常歡迎客戶來參觀和檢查工廠。請聯絡我們的銷售經理 Lisa (信箱: lisa@busbarmachine.co) 並告訴我們您的日程安排。我們將向您發送正式的商務邀請函。
我可以成為你們工廠在我國的經銷商嗎?
非常歡迎您申請成為我們母線機經銷商,共同開發海外市場。我們將提供豐厚的銷售佣金和額外的現金獎勵。具體合作內容及方式請聯絡我們CEO Robin(信箱: ceo@busbarmachine.co).